Please update your browser.
Findings
- Go to finding 1各城市在地方商业上的支出同时下降, 尤其是低收入社区.
- Go to finding 2Online local commerce spend grew by 1.5%的线下消费急剧下降,而线上消费份额增长了4%.6 percentage points.
- Go to finding 3 Only grocery and pharmacy spend grew materially, 线上增长至少是线下增长的三倍.
- Go to finding 4 Approximately 8 percent of LC spend shifted from restaurant to grocery spend; local access to groceries varied widely by neighborhood income quintile and across cities.
COVID-19 has rapidly transformed everyday life. 虽然大流行的范围是全球性的,但消费者在当地受到经济影响. 要了解COVID-19对当地经济造成的压力,需要从地方的角度来看待社区内消费者和商家之间的相互作用, 哪些可以为正在进行的帮助当地经济复苏的努力提供信息.
这一见解利用了2019年10月至2020年3月期间,来自1100万大通客户的每月约4.5亿笔信用卡交易样本的本地商业数据集. 本地商业视图表示本地买家和卖家之间交易的日常商品和服务,并包括进行交易的渠道(在线/离线)以及消费者和商家的邮政编码, 了解消费者居住地与购买地点之间的距离.
这一见解的目的是告知疫情对美国各地当地商业供需的影响.S. cities, 包括对高收入社区和低收入社区的分析, access to food, shifts in the types of products and services purchased, and shifts from brick-and-mortar to online.
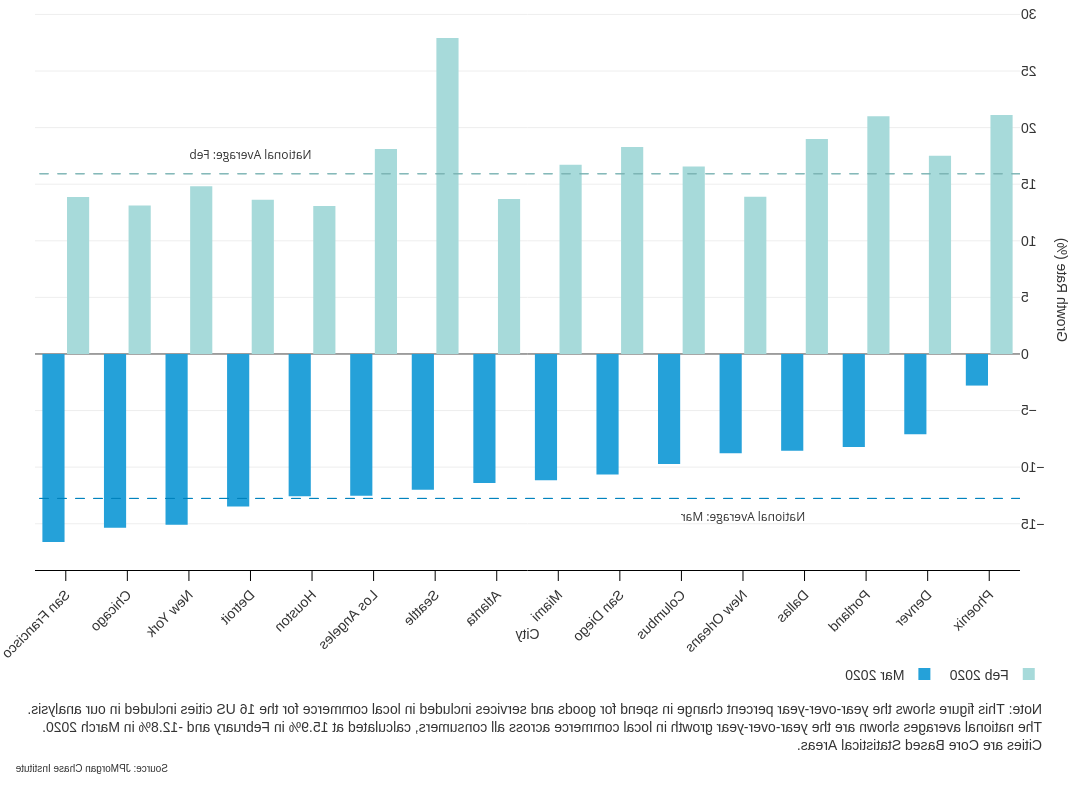
Finding One: 各城市在地方商业上的支出同时下降, 尤其是低收入社区.
- Local commerce spend declined by 12.8 percent between March 2019 and March 2020.
- San Francisco, Chicago, New York, 底特律的当地商业支出下降幅度最大.
- 低收入社区经历了不成比例的支出大幅下降,降幅超过15%.
按城市分列的当地商业支出同比变化百分比
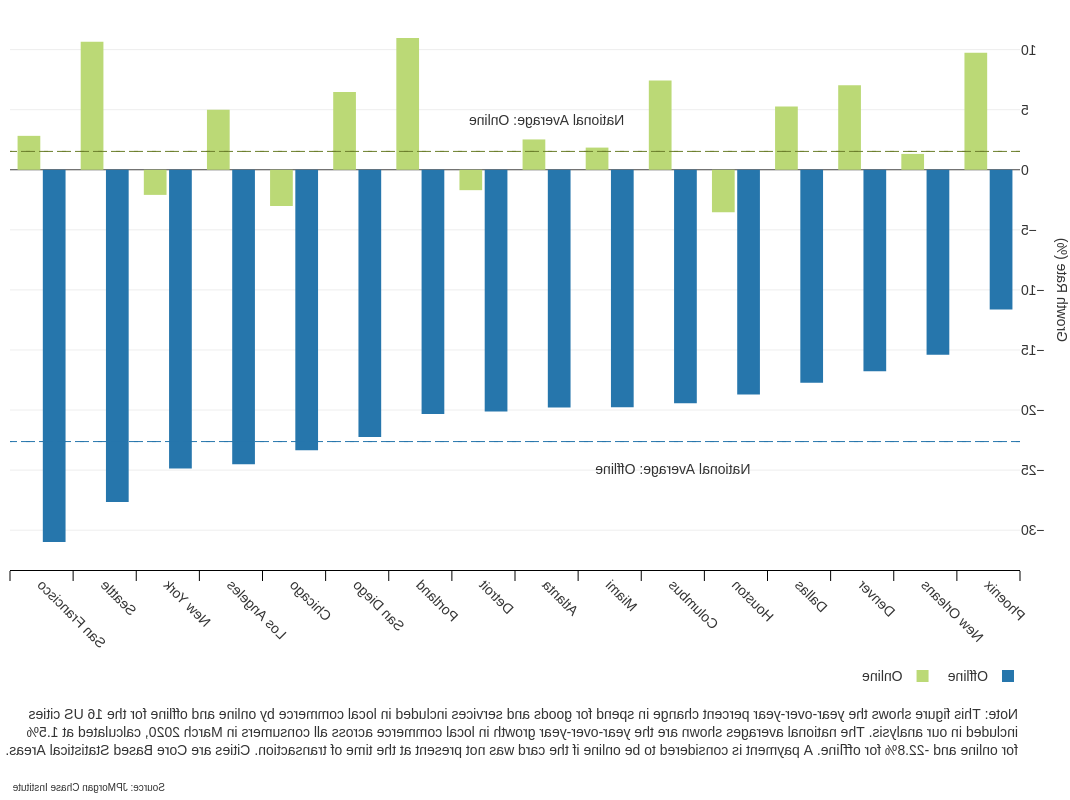
Finding Two: Online local commerce spend grew by 1.5%的线下消费急剧下降,而线上消费份额增长了4%.6 percentage points.
- The online share of local commerce spend grew from 42.9 percent in February 2020 to 47.5 percent in March.
- Offline spending decreased the most in San Francisco (-31.0 percent), Seattle (-27.7 percent), New York (-24.9 percent), and Los Angeles (-24.5 percent).
- 低收入社区最有可能经历网上消费的大幅下降.
按渠道分列的本地商业支出同比变化百分比
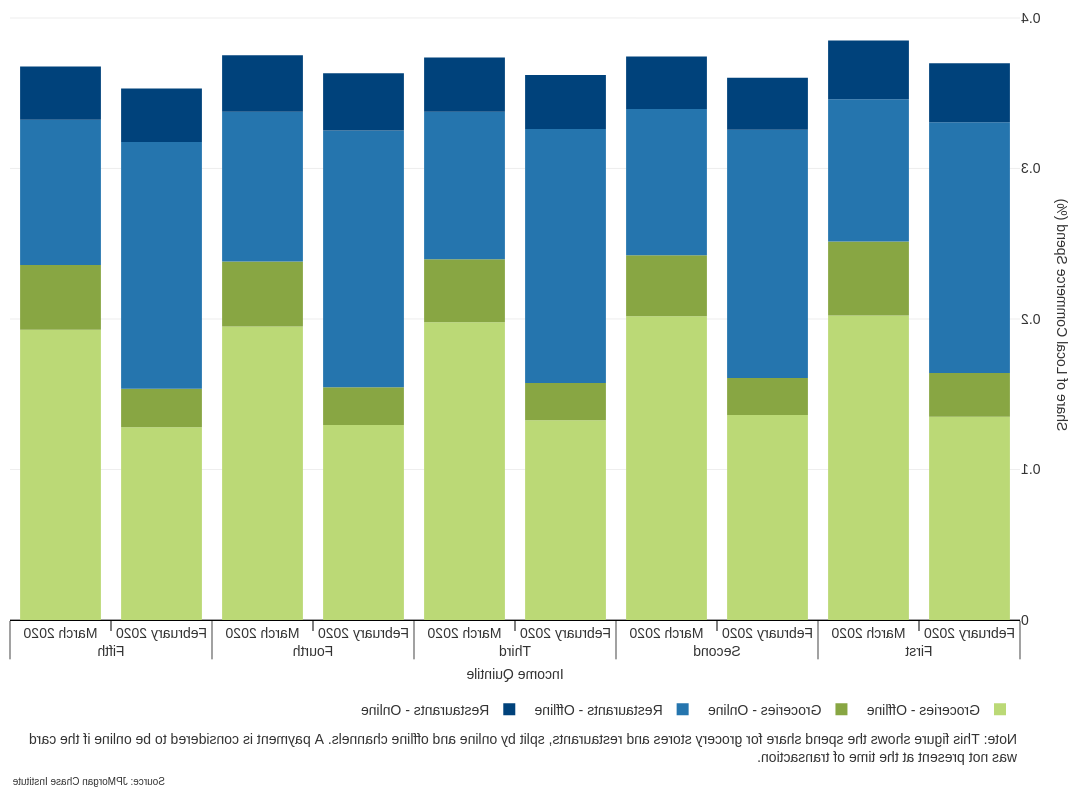
Finding Three: Only grocery and pharmacy spend grew materially, 线上增长至少是线下增长的三倍.
Finding Four: Approximately 8 percent of LC spend shifted from restaurant to grocery spend; local access to groceries varied widely by neighborhood income quintile and across cities.
Authors
Chris O. Wheat: JPMorgan Chase Institute
Marvin M. Ward Jr.: JPMorgan Chase Institute
Lindsay E. Relihan: London School of Economics &
Centre for Economic Performance